Avoid Long Controller Paths In Laravel Routes

Certainly! Here’s an example of how you can use the namespace of controllers at the top of your route file to avoid long controller paths:
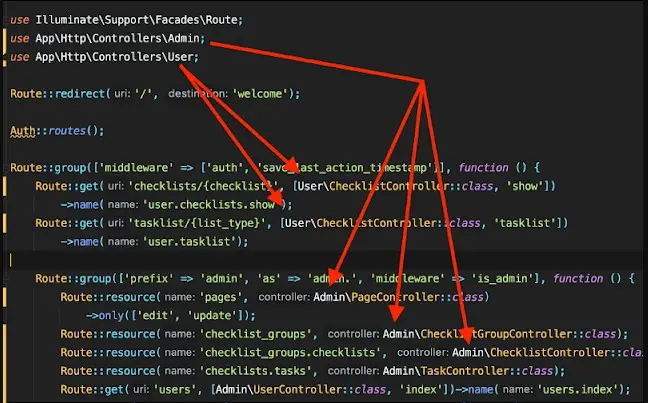
Namespace of controllers at the top of your route file
<?php
// Import the necessary classes and namespaces
use App\Http\Controllers\ExampleController;
use App\Http\Controllers\AnotherController;
// Set the namespace for your controllers
$namespace = 'App\Http\Controllers';
// Define your routes
Route::namespace($namespace)->group(function () {
// Routes within this group will have the 'App\Http\Controllers' namespace automatically applied
Route::get('/example', [ExampleController::class, 'index']);
Route::post('/example', [ExampleController::class, 'store']);
Route::get('/another', [AnotherController::class, 'index']);
Route::post('/another', [AnotherController::class, 'store']);
// More routes...
});
To avoid long controller paths in Laravel routes, you can make use of route closures or the “Route::namespace” method. Here’s how you can achieve it:
Route Closures
Instead of specifying a controller and method directly in your route definition, you can use a closure to define the route logic inline. Here’s an example:
Route::get('/example', function () {
// Your route logic here
});You can define the closure directly in your route file or extract it to a separate closure function if needed.
Route Namespace
If you have multiple routes that belong to the same namespace, you can use the “Route::namespace” method to specify the namespace once and reduce the length of the controller path for subsequent route definitions. Here’s an example:
Route::namespace('App\Http\Controllers')->group(function () {
// Routes within this group will have the 'App\Http\Controllers' namespace automatically applied
Route::get('/example', 'ExampleController@index');
Route::post('/example', 'ExampleController@store');
// More routes...
});By wrapping your routes within the “Route::namespace” group, you can avoid repeating the full controller path for each route definition.



I could not refrain from commenting. Perfectly written!